Advanced Biological Research System (ABRS)
Spaceflight Research Tool
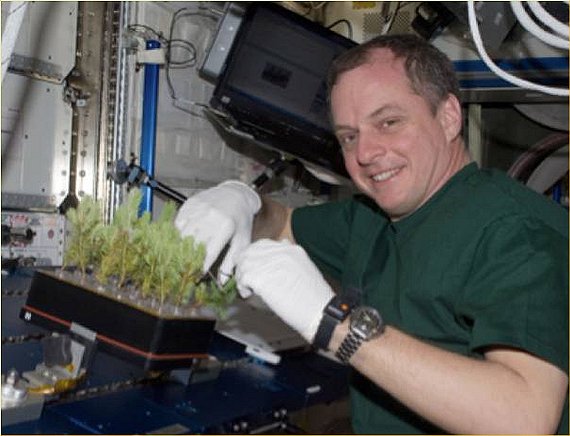

- Confirmed Plants Grown:
- White Spruce Trees
- Key Features:
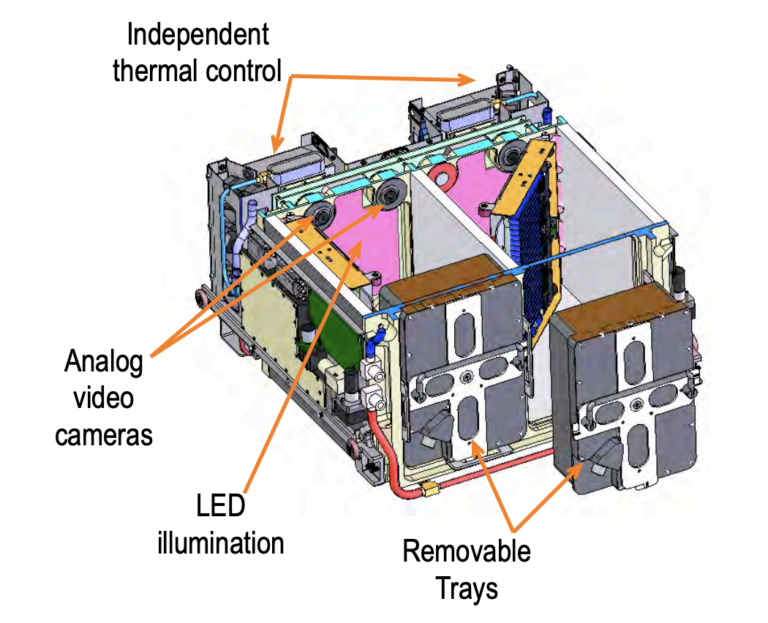
- Temperature Control
- In-unit lighting
- Ethylene, VOC removal
- Optional green fluorescent protein (GFP) imaging system
- 3 cameras
- Condensate recovery and automated water reintroduction
Summary
The Advanced Biological Research System (ABRS) is a piece of technical hardware used for the growth of various biological organisms. It is installed on the International Space Station. White spruce trees have been grown in ABRS.
Here is a description of the locker from NASA’s mission page.
“The Advanced Biological Research System (ABRS) is a single-middeck-locker replacement facility. As a middeck locker replacement, the ABRS is compatible with both the space shuttle and the International Space Station (ISS) EXpedite the PRocessing of Experiments to Space Station (EXPRESS) rack. In the middeck, the ABRS is a rear-breathing, powered locker that can be used as a primary facility or as a specimen transportation device. In the EXPRESS rack, the ABRS is a subrack facility payload that takes advantage of both rear air breathing and intercooling via the moderate temperature loop. Sensor data and images are conveyed through the EXPRESS rack to the ground via Ethernet. The ABRS may be commanded from the ground or by the crew using an EXPRESS laptop. The current operating scenario includes a low-power ascent mode in the middeck and permanent residence on the ISS.
Each ABRS Environmental Research Chamber (ERC) can independently provide the following services:
- Temperature control to 8 °C below ambient
- PAR of 50 to 300 micromol/m2/sec illumination
- Continuous removal of ethylene to less than 25 parts per billion (ppb)
- Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) control
- Continuous removal of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
- Relative humidity control to between 60 and 90 percent
- Generic chamber imaging from three cameras
- Generic support of experiment-unique equipment, including a Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) imager.”