SVET Plant Growth System
Spaceflight Research Tool

- Full Name: SVET (свет: translation: light)
- A.K.A: SVET SG, SVET-2, SVET-2 SG
- Affiliation: NASA, Roscosmos
- Country: United States, Russia, Bulgaria
- Focus Areas: Plant Habitat
- Type: Spaceflight
- Spacecraft: MIR
- In Service: 1990-2001
- Predecessor: Fiton/Phyton
- Successor: Lada
- Confirmed Plants Grown:
- Wisconsin Fast Plants (Brassica rapa)
- Dwarf wheat
- Accolades:
- First seed-to-seed plant growth experiment in space
- Key Features:
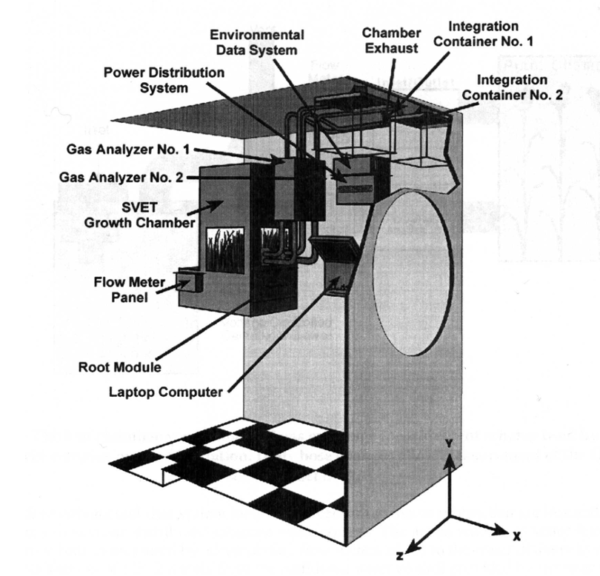
- GEMS (Gas Exchange Measurement System)
- Root Module
- In-unit lighting (Illumination Unit)
Summary
The SVET (свет: Russian: light) plant growth system was a small greenhouse module on the Russian spacecraft MIR. Some of the first advanced astrobotany experiments took place in SVET. SVET was installed in 1990 and was located in the Kristall module of Mir and consisted of 4 basic units:
- the plant growth chamber itself
- the root module
- the light and control unit
- the GEMS (Gas Exchange Measurement System)
Plant varieties such as dwarf wheat and Brassica rapa were grown in SVET, with important variables being controlled and measured using this equipment. Substrate moisture was one of those being studied.
SVET was upgraded under a Bulgarian-American contract prior to a 1997 experiment involving Brassica rapa. SVET-2 included a brighter illumination unit and updated root modules.